Introduction
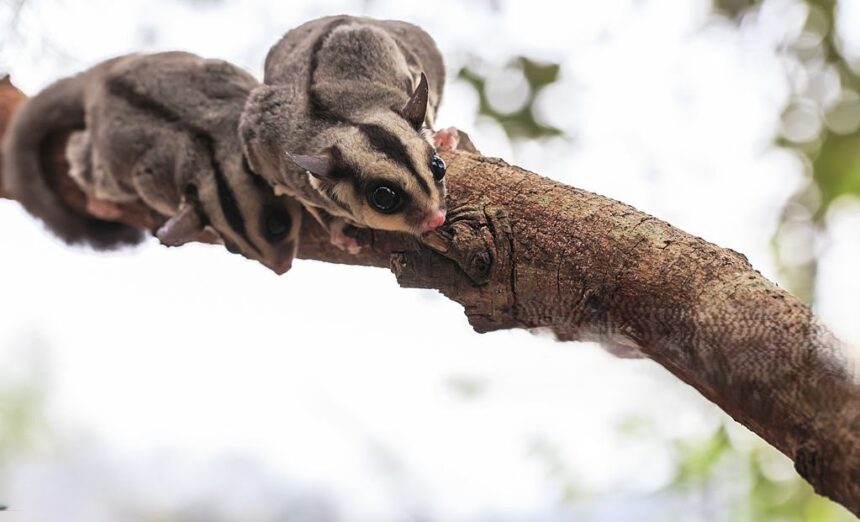
Sugar gliders are small, fascinating marsupials known for their playful personalities and unique ability to glide through the air. As exotic pets, many owners often wonder — how long do sugar gliders live? On average, these charming creatures live 12 to 15 years in captivity, while those in the wild typically reach around 9 years. Their lifespan largely depends on proper diet, safe housing, and regular veterinary care. Understanding what affects a sugar glider’s life expectancy helps owners provide better environments where these affectionate companions can thrive and live long, healthy, and joyful lives.
Understanding Sugar Gliders
Sugar gliders are small nocturnal marsupials native to Australia, Indonesia, and Papua New Guinea. They get their name from their love for sweet foods and their ability to glide through the air using a thin membrane between their limbs. Known for their playful and social behavior, sugar gliders live in family groups in the wild and form strong bonds with their owners in captivity. Their unique biology, active nature, and affectionate personality make them popular exotic pets for people who can provide dedicated time and proper care.
How Long Do Sugar Gliders Live?
The average sugar glider lifespan varies depending on where they live. In the wild, these tiny marsupials usually live up to 9 years, facing predators and harsh conditions. However, in captivity, with proper diet and veterinary care, they can live between 12 to 15 years, and some even reach 18 years. Their life expectancy improves greatly when owners maintain clean habitats, offer balanced nutrition, and ensure social interaction. Understanding these differences helps pet owners provide the best care to help sugar gliders live longer, healthier lives.
Factors That Affect Lifespan
Several factors play a major role in determining how long sugar gliders live. A balanced diet rich in protein, fruits, and insects supports strong bones and energy. The living environment also matters — a clean, spacious cage with proper temperature (75–90°F) and daily enrichment keeps them happy. Regular veterinary checkups help detect health issues early, while genetics and breeding quality influence overall lifespan. When owners combine proper nutrition, hygiene, and medical care, their sugar glider’s life expectancy can reach its full potential.
Health Risks and Common Diseases
Like all pets, sugar gliders face certain health problems that can affect their lifespan. Poor diet may lead to malnutrition or metabolic bone disease, while lack of hygiene can cause infections or parasites. Obesity, dental issues, and a condition called “Ick” are also common in captivity. Regular vet visits, clean cages, and a proper diet are key to prevention. Watching for early signs like hair loss, weakness, or appetite changes helps owners act quickly, improving their sugar glider’s health and life expectancy.
How to Improve Sugar Glider Longevity
To help your sugar glider live longer, focus on consistent daily care. Spend at least one to two hours interacting with them to strengthen social bonds and reduce stress. Feed a nutritious mix of fruits, vegetables, and protein while avoiding processed foods. Keep their cage clean — remove waste daily and deep-clean every two weeks. Maintain a warm, safe environment between 75–90°F. Regular vet checkups and a stimulating habitat with toys and climbing areas can greatly extend your sugar glider’s lifespan and happiness.
Sugar Glider Life Stages
A sugar glider’s life moves through several stages, each with unique needs. Babies, called joeys, stay in their mother’s pouch for about two months before exploring. As juveniles, they learn to glide, eat solid foods, and become more active. Adults are playful, social, and reach full size within a year. Senior gliders slow down, sleep more, and may need softer foods. Understanding these life stages helps owners provide age-appropriate care, ensuring their sugar glider’s lifespan remains healthy and fulfilling from birth to old age.
Breeding and Lifespan
Breeding can affect a sugar glider’s lifespan, especially for females. Their short pregnancy lasts about 16 days, followed by two months of pouch care for the babies, called joeys. Overbreeding or poor nutrition can cause stress and health issues, shortening life expectancy. Responsible breeding should always follow USDA guidelines and avoid unsafe color-pair genetics. Hobby breeders and pet owners should allow rest periods between litters and focus on proper diet and environment. Ethical breeding practices help maintain healthy, long-living sugar glider generations in captivity.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Before owning or breeding sugar gliders, it’s important to understand legal and ethical rules. In some U.S. states, like California and Pennsylvania, owning a sugar glider is illegal due to wildlife regulations. Always check local and federal laws before buying or breeding. Ethical ownership means purchasing from licensed, reputable breeders instead of wild-caught sources. Responsible care, proper housing, and humane treatment ensure sugar gliders live safe and happy lives. Following these laws and ethics helps protect both the species and your sugar glider’s longevity.
Extending Lifespan Through Enrichment
Keeping your sugar glider active and engaged is one of the best ways to support a long, healthy life. Provide toys, ropes, and safe branches for climbing and chewing. Rotate enrichment items often to keep their environment exciting. Offer supervised playtime outside the cage in a secure room to encourage movement and bonding. Mental stimulation reduces boredom, which can lead to stress and illness. A happy, curious glider that plays daily and enjoys social interaction will naturally have a longer and healthier lifespan in captivity.
Sugar Glider Lifespan Compared to Other Pets
When comparing sugar glider lifespan to other small pets, they stand out for their longevity. While hamsters live 2–3 years and ferrets about 6–8 years, sugar gliders can thrive for 12–15 years in captivity. This longer life comes from their marsupial biology, balanced diets, and safe indoor environments. Providing mental stimulation, companionship, and routine vet care helps them live much longer than most pocket pets. Understanding these differences highlights how proper care and environment make a significant impact on a sugar glider’s life expectancy.
FAQs
- What shortens a sugar glider’s life?
Poor diet, lack of vet care, and stress.
2. Can sugar gliders live alone?
No, they need companions for emotional health.
3. How do I know if my glider is aging?
Watch for less activity, dull fur, or slower movement.
4. What diet helps them live longer?
A balanced mix of fruits, insects, and protein.
5. Are sugar gliders good for beginners?
Yes, but they require daily care, bonding, and a proper environment for a long lifespan.
Conclusion
Caring for a sugar glider is both rewarding and long-term. With the right diet, environment, and veterinary care, these playful marsupials can live up to 15 years or more. Their lifespan depends on love, attention, and consistent care from their owners. By providing a safe home, daily interaction, and nutritious food, you help ensure your sugar glider lives a happy, healthy life. Remember, commitment and compassion are key to giving these fascinating pets the long, fulfilling lives they truly deserve.